“Cyberwarfare in 2025: How Ukraine & Russia”

INTRODCUTION
Modern warfare includes cyberwarfare as a critical front since Ukraine and Russia continue their Cyberwarfare in 2025. Both countries remain in a continuous digital contest in which critical infrastructure suffers damaging attacks and fraudulent information spreads through AI systems, while producing worldwide effects. Multiple hacking groups supported by states and volunteer technicians joined with new-generation malware attacks, which transform the ways hostile operations occur while threatening vital power networks and banking systems. The invisible battle space reveals which power remains superior. The digital combat between these nations affects global systems, which part does it modify? This article analyzes the developing cyber conflict that the Ukraine-Russia war in 2025 showcases, while exposing its principal approaches and dangerous strategies, and security threats.
1. Always-Listening Devices: Your Voice Assistant Knows Too Much
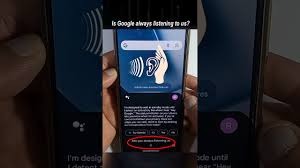
Voice assistants represented by Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple’s Siri have become popular home fixtures, allowing users to manage their smart devices without touching anything. The continuous active mode of these devices allows them to detect “Hey Siri” or “Alexa,” but their hidden flaw includes substantial audio storage beyond user expectations.
According to a 2024 study conducted by Northeastern University, researchers discovered that smart speakers mistake background sounds such as TV shows and laughter or stray words as intended wake commands, after which they record private conversations by mistake. Security flaws in voice assistant devices enable hackers to steal personal information, such as spoken credit card data and private business talks
The risks don’t stop there. Third-party “skills” or apps, many of which request unnecessary permissions, have been caught surreptitiously harvesting audio data. In one notorious 2023 case, a fake meditation app for Alexa was caught recording users and selling the data to advertisers. Even when companies promise encryption, cloud storage breaches (like the 2022 Alexa voice data leak) expose recordings to Cyberwarfare in 2025.
2. Smart Cameras & Baby Monitors: When Your Home Surveillance Turns Against You
The trend of installing home security cameras and baby monitors to achieve peace of mind has transformed into one of the major privacy liabilities within smart homes by 2025. Your family safety devices, which serve as a surveillance tool, are now being exploited by hackers because of which turn against your protection instead of protecting you.
The dangers presented are actual rather than theoretical. A popular baby monitor brand revealed its 200,000 user live video feeds to strangers in 2023 so they could watch sleeping infants and overhear family conversations and broadcast sound through the built-in speakers. Hackers gain access to cameras by entering default passwords like “admin” or “1234” because many users avoid password changes. The dark web has become a marketplace where cybercriminals save and profit from stolen footage, which some criminals use to engage in blackmail behavior and harassment practices.
Smart cameras that cost under 100 dollars face two major security issues since they have insecure Wi-Fi transmission and no encryption functionality. Hooked-up firmware in costly devices prompts hacker access since firmware updates prevent security holes. Research has uncovered manufacturer practices that secretly upload recorded footage to remote servers where users cannot provide their explicit consent, thus generating another security concern.
3. Smart TVs & Streaming Devices: Ads That Know Too Much
A smart TV functions as an advanced monitoring device that transforms into a basic flat screen when inactive. Modern smart TVs and streaming devices monitor everything you watch as well as your watch time and conversation content for purposes of “personalized advertising.” A 2025 FTC investigation revealed that 87% of smart TVs collect and sell viewer data to advertisers, data brokers, and even third-party analytics firms. Some budget brands have been caught secretly recording ambient conversations through built-in microphones, even when voice control features were supposedly disabled.
The tracking happens through Automatic Content Recognition (ACR), a technology that scans every frame of content, whether from Netflix, cable TV, or even your gaming console, to build detailed profiles of your viewing habits. Worse yet, many smart TVs share this data over unsecured connections, making it easy for hackers to intercept. In 2024, a vulnerability in a popular TV brand’s software allowed cybercriminals to hijack screens, display ransomware demands, or even spy on users via the built-in camera. Meanwhile, malicious apps disguised as streaming services have been caught injecting ads with tracking malware, turning your binge-watching session into a privacy nightmare.
4. Smart Locks & Garage Doors: Digital Break-Ins Are Real
The promise of keyless entry has a dangerous flaw: your smart lock might be giving hackers a VIP pass to your home. In 2025, cybersecurity researchers have demonstrated how Bluetooth and Wi-Fi-enabled smart locks can be bypassed in under 30 seconds using simple replay attacks or brute-force password cracking. One alarming study found that nearly 40% of smart lock owners never changed their default PIN codes, leaving doors vulnerable to anyone who knows the manufacturer’s standard combinations (like “0000” or “1234”). Even high-end biometric locks aren’t immune – researchers at DEF CON showed how fingerprint sensors can be fooled with basic 3D-printed replicas.
The vulnerabilities extend beyond front doors. Smart garage door openers using unencrypted radio signals have been hijacked using cheap hardware available online, allowing thieves to discreetly enter homes without triggering alarms. In a notorious 2024 case in Seattle, a burglary ring used a $50 radio transmitter to capture and replay signals from luxury homes’ garage systems. Many IoT door systems also suffer from poor firmware update mechanisms, meaning critical security patches often go uninstalled for months or years. Perhaps most disturbingly, some cloud-connected locks have been compromised through their companion apps, with hackers gaining remote access to homes thousands of miles away.
5. Router Vulnerabilities: The Weakest Link in Your Smart Home
Your router is the digital front door to your smart home, and in 2025, it’s become the #1 target for cyberattacks. Shockingly, 60% of IoT breaches originate through compromised routers, turning these unassuming boxes into gateways for hackers to infiltrate every connected device in your home. Customers frequently keep the poor routers provided by ISPs, which rarely obtain security updates and contain weak passwords set to “admin/admin”. Once control is seized over the outer, attackers gain the ability to redirect web traffic toward phishing sites and plant malware into your downloads, as well as monitor your smart home devices. Cyberwarfare in 2025
The threats are evolving rapidly. The rise in DNS hijacking attacks, which redirect browser traffic toward malicious sites that develop fake versions of banking and social media websites, has risen 300% since the beginning of 2023. The dark web hosts zero-day vulnerabilities from popular router models that remain unfixed for months. The botnet network utilized out-of-date routers to conduct attacks against smart homes by simultaneously unlocking doors as part of Cyberwarfare in 2025. disabling cameras, and triggering false fire alarms as a distraction for physical break-ins. Even scarier? Many routers lack proper encryption, allowing nearby hackers to intercept sensitive data, from your smart thermostat settings to your baby monitor feeds, with basic wireless sniffing tools.
Pros and cons
Pros of Smart Home Routers
- Centralized Control – A single router manages all your IoT devices, making network-wide security updates and monitoring easier.
- Advanced Security Features – Modern routers offer firewalls, VPN support, and device isolation to protect against attacks.
- Convenience – Remote management via apps allows quick troubleshooting and security adjustments from anywhere.
- Guest Network Isolation – Keeps visitors (and potential threats) separate from your main smart home devices.
- Traffic Monitoring – Some routers provide real-time alerts for suspicious activity, helping detect breaches early.
Cons of Smart Home Routers
- Single Point of Failure – If hacked, the router exposes every connected device (cameras, locks, assistants).
- Outdated Firmware Risks – Many routers, especially ISP-provided ones, rarely receive critical security patches.
- Weak Default Settings – Manufacturers often ship routers with easily guessable admin passwords (e.g., “admin/admin”).
- DNS Hijacking Vulnerabilities – Hackers can redirect traffic to fake sites and steal login credentials.
- Limited Consumer Awareness – Most users never check router settings, leaving them open to exploitation.
CONCLUSION
Cyberwarfare in 2025 was largely formed through the Ukrainian-Russian conflict. The initial Russian espionage and disruptive attacks have transformed into a continuous war of attrition that uses artificial intelligence systems. Where civilian infrastructure, private tech firms, and hacktivist collectives have become frontline participants. Ukraine’s unprecedented cyber resilience-bolstered by global alliances and crowdsourced defense, has proven that decentralized, agile responses can counter even state-sponsored aggression. Meanwhile, Russia’s escalation of destructive wipers, deepfake propaganda, and supply chain assaults has erased any remaining boundaries in cyber conflict, normalizing attacks on critical systems worldwide. As AI accelerates offense and defense alike, and as mercenary hacking groups blur the lines between crime and warfare.










1 thought on ““Cyberwarfare in 2025: How Ukraine & Russia Changed Hacking Forever””