Ransomware Attacks in 2025:

INTRODUCTION
All stakeholders, including small enterprises and multinational corporations, face hazardous Ransomware Attacks in 2025 as major cyber threats in 2025. The attacks now go beyond file encryption to steal data and interrupt operations because attackers demand enormous payments that modern cryptocurrency systems make difficult to trace. Through double extortion schemes, cybercriminals enhance their threats by leaking stolen information unless ransom payments are received, which results in increased victim pressure. The entire spectrum of organizations, from healthcare facilities to academic institutions to governmental departments, has become targeted by victims of damaging intrusions, which establish universal susceptibility. AI tools serve as valuable resources for hackers who utilize artificial intelligence to create stealthy phishing communication that fools many users. The availability of Ransomware-as-a-Service tools through the Internet allows unskilled criminals to launch advanced attacks easily.
The increasing average ransom payments now reach millions, causing devastating impacts on both business finances and public image. The data recovery rate among victims who decide to pay remains poor as they continue to remain exposed to secondary cyberattacks. The good news? Secure cybersecurity measures serve to decrease operational risk levels. This guide explains ransomware operation in 2025 while offering concrete measures for data protection as well as business defense.
The State of Ransomware in 2025
1. More Targeted, More Destructive
Fishermen no longer use random tactics when trapping victims through their phishing emails. Ransomware groups today spend time on strategic research to specifically choose assets which include medical facilities as well as financial institutions and essential infrastructure. The attackers identify and attack vulnerabilities through non-updated software or mismanaged cloud platforms as well as through employee access grants.
A major U.S. hospital chain encountered a ransomware attack back in early 2025 which rendered patient care disrupted for numerous weeks. The hackers demanded $10 million ransom before they released patient medical records after the financial demand was not fulfilled.
2. Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) is Booming
Today’s attackers do not require any specific computer knowledge to deploy cyber attacks. Dark web vendors provide Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) ransomware kits giving unskilled hackers the ability to launch serious malware attacks. Such kits provide round-the-clock customer assistance with payment portals and they also offer negotiation capabilities.
Research indicates RaaS operations will make over $1 billion in annual revenue by 2025, according to Cybersecurity Ventures.
3. Double and Triple Extortion Tactics
Modern ransomware gangs don’t just encrypt files—they:
- Steal data and threaten to leak it (double extortion).
- Contact customers or partners to pressure victims into paying (triple extortion).
- Launch DDoS attacks to further cripple operations.
Case Study: A European manufacturing company paid a $2 million ransom, only for hackers to return months later, exploiting the same vulnerability.
How Ransomware Attacks Happen
Getting familiar with the attack patterns makes it simpler to prevent security breaches. Here’s how most breaches occur:
- The initial stage of access occurs when attackers use phishing emails with stolen credentials along with software vulnerabilities that remain unpatched.
- As part of their strategy, hackers traverse the network to achieve greater access privileges for critical systems.
- Data Exfiltration treats sensitive files as the first priority for data theft before encryption occurs.
- The deployment of Ransomware results in system locking with the appearance of a ransom notification.
How to Protect Yourself in 2025

1. Patch Everything—Religiously
One of the most effective ways to prevent ransomware attacks is to patch all software and systems immediately-cybercriminals often exploit known vulnerabilities that have existing fixes. A 2024 study found that 60% of ransomware breaches could have been prevented if victims had installed available security updates on time.
Pros:
- Proactive patching slashes attack risks but demands constant vigilance.
- Employee training reduces human error yet requires ongoing investment.
- Air-gapped backups guarantee recovery but complicate data accessibility.
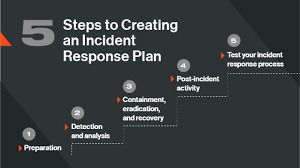
- Incident response plans minimize downtime, though they need regular testing.
Cons:
- Zero-trust models boost security but slow down workflows.
- Cyber insurance covers losses, yet may incentivize ransom payments.
- AI threat detection spots attacks early but generates false alarms.
- Law enforcement collaboration helps investigations, but rarely recovers funds
CONCLUSION
The Ransomware Attacks in 2025 showcase sophisticated traits because attacks have risen by 35% per year, and criminals now demand over $1.5 million on average for ransom (Coveware, 2025). The combination of multiple defense mechanisms, which includes system updates and employee training in addition to backup separation and incident response preparedness, enables organizations to prevent successful ransomware attacks by 83% (Cybersecurity Ventures, 2025). Active precaution practices create substantial improvements to organizational resilience, even though complete security measures remain impossible. The key takeaway? The tactics of cybercriminals advance constantly, but businesses capable of preparation will protect themselves from easy targeting. Your defense readiness should begin immediately instead of waiting for a cyber attack to occur.










People should become aware of using any digital device for avoiding this such kind of incidents. This is a tremendous article for enhancing cyber awareness.
This article gave me a fresh perspective! The insights are clear and well-explained. I appreciate the effort behind such valuable content. Looking forward to more posts like this!
Great article! The discussion on the rise of ransomware attacks and the defense strategies was very insightful. I especially appreciated how the importance of combining preventive measures with internal organizational preparedness was emphasized. It’s urgent for companies to take cybersecurity seriously and adopt a more proactive approach. Congratulations on the informative and timely content!
Thank You Very Much For your Appreciation!
A very relevant article! With ransomware threats growing in 2025, awareness, regular backups, and smart cyber practices are more important than ever. Thanks for the practical tips!
In the world of full of scams, this post is blessings.
Thank you for informing this. I will be careful
Very nice. The article was great
This article shows us about how to avoid cyber attacks and surfing carefully.
This is some valuable information. We need more articles like this.
These articles are very good, the content is very rich and useful. I will follow the blog to be able to read more good and useful articles like this many more times.
Insightful read! AI-driven ransomware and supply chain attacks are a real wake-up call. Solid tips on staying protected—backup, patch, and use smart detection tools!
Very blessing article
Your creativity is inspiring
Very informative and helpful content is this
Great articles