Why Cybersecurity Insurance Is the Hottest Trend
INTRODUCTION
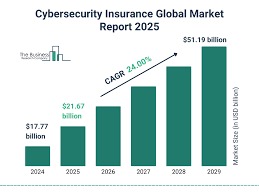
Picture waking up to find your business paralyzed, Why Cybersecurity Insurance customer data stolen, systems locked by ransomware, and a six-figure demand blinking on every screen. Now imagine having a financial lifeline that covers the ransom, handles legal fallout, and even repairs your reputation. This is the reality of cybersecurity insurance in 2025, the fastest-growing protection trend as digital threats evolve from possibility to inevitability. With ransomware attacks now striking every 11 seconds and AI-powered scams making everyone a potential target, cyber insurance has shifted from luxury to necessity-but with confusing policies, rising premiums, and controversial fine print, is it truly the safety net businesses and individuals need, or just another cost of doing business in our vulnerable digital world? As we peel back the layers of this booming $45 billion industry, we’ll help you answer one critical question
1. Why Cyber Insurance Is Going Mainstream in 2025
The Perfect Storm Driving Demand
Three key factors are fueling the cyber insurance rush:
1. Ransomware Epidemic
- Attacks now happen every 11 seconds (Cyber Ventures, 2025).
- Average ransom demand: $ 1.5 M+ for mid-sized businesses.
2. Regulatory Pressure
- Laws like GDPR and NYDFS now require Why Cybersecurity Insurance for certain industries.
- Class-action lawsuits over data breaches are skyrocketing.
3. AI Lowers the Barrier for Hackers
- Tools like WormGPT let amateurs launch sophisticated attacks.
- Deepfake fraud (e.g., fake CEO voice scams) is now insurable.
Case Study: A bakery chain’s smart fridge network got hacked in 2024, leaking customer payment data. Their $2M cyber policy covered forensics, legal fees, and even cookie giveaway PR campaigns to rebuild trust.
2. What Cyber Insurance Actually Covers (And What It Doesn’t)

Typical Coverage
| Coverage Type | What It Pays For |
|---|---|
| Ransomware | Ransom payments, data recovery |
| Data Breaches | Customer notifications, credit monitoring |
| Business Interruption | Lost income during downtime |
| Legal Fees | Lawsuits, regulatory fines |
| Reputation Repair | PR crisis management |
Common Exclusions
Negligence (e.g., ignoring software updates)
Pre-existing breaches (you can’t insure a hack that already happened)
War/state-sponsored attacks (e.g., Russian hackers targeting US grids)
3. Who Needs Cyber Insurance in 2025?
Businesses (Non-Negotiable If You…)
- Handle customer data (emails, credit cards, health records).
- Rely on cloud services (AWS, Shopify, etc.).
- Use IoT devices (smart security cams, inventory trackers).
FYI: 74% of SMBs hit by ransomware close within 6 months (FBI 2024).
Individuals (Worth Considering If You…)
- Are a high-net-worth target (e.g., crypto investors, execs).
- Run a side hustle (Etsy, OnlyFans, freelance consulting).
- Own smart home gadgets (hacked doorbells can lead to liability claims).
4. The Dark Side: Why Some Hate Cyber Insurance
Controversy 1: Are We Just Funding Hackers?
Critics argue that paying ransoms fuels more attacks. Some insurers now require victims to try recovery first.
Controversy 2: Skyrocketing Premiums
- Rates jumped 120 %+ since 2023 (McKinsey).
- Insurers now scan your network before offering quotes (like a health exam for your servers).
Controversy 3: Coverage Gaps
- AI-related claims are often disputed (Was it a “hack” or just a chatbot gone rogue?).
- Supply chain attacks may not be covered (e.g., SolarWinds-style breaches).

Here are the trends we examine in the Guide:
- Data Collection: Cyber insurance coverage for wrongfully collected information—collecting personal information without the individual giving proper consent—is unsettled at best. Data collection is the most consistent coverage aspect that needs negotiation throughout 2024, and the trend is likely to continue this year.
- Security Tools: In 2024, multiple carriers started offering some cybersecurity tools directly, positioning their cyber insurance product as a backstop to protecting businesses. This trend will continue in 2025.
- CISO Coverage: Coverage for chief information security officer (CISO) liability can be found in both cyber policies and well-brokered directors and officers (D&O) policies. Some carriers are now offering a stand-alone policy to cover CISO personal liability.
- Third-Party Risks: Cyber insurance carriers are looking for clients to have a robust third-party risk management program that includes strong contractual language, cybersecurity certifications from vendors, and requirements for vendors to purchase cyber or technology errors & omissions (E&O) insurance.
The Pros and Cons of Cybersecurity Insurance in 2025
PROS:
Today, Why Cybersecurity Insurance serves as a vital protection against disastrous ransomware attacks and data breaches, along with legal consequences that otherwise could destroy businesses or individuals. Companies survive or go bankrupt after dealing with six-figure ransom demands or regulatory fines through insurance protection. Policies now cover everything from forensic investigations to PR crisis management, while some even provide 24/7 access to incident response teams valuable resource for organizations without in-house security experts. Individuals, particularly high-net-worth targets or those running online businesses, benefit from identity theft restoration and fraud reimbursement. The surge in AI-powered attacks and strict data protection laws has made coverage practically mandatory for many industries, with some insurers even helping clients improve their security posture to prevent claims.
CONS:
The cons reveal significant challenges: soaring premiums (up 120% since 2023) and increasingly strict requirements, like mandatory multi-factor authentication, that exclude smaller businesses. Critics argue insurers are fueling ransomware gangs by approving payouts, while others highlight coverage gaps for emerging threats like AI-driven social engineering or state-sponsored attacks. Many policies deny claims for “negligence,” leaving victims unprotected if they missed software updates or employee training. For individuals, the costs may outweigh the benefits unless they’re high-risk targets. Ultimately, cyber insurance isn’t a magic shield- it works best when paired with robust security measures, not as a replacement for them.
CONCLUSION
Cybersecurity insurance has undeniably become a necessary layer of protection in our hyper-connected world, acting as a financial airbag when preventative measures fail. For businesses, it’s increasingly non-negotiable – the potential costs of a single breach could dwarf years of premium payments. Yet this protection comes with caveats: rising costs, complex requirements, and the uncomfortable reality that some policies may inadvertently fund the very criminals they’re meant to protect against. The most prudent approach combines robust security practices with carefully vetted insurance as a last line of defense. As threats evolve, so must policies – what’s covered today might be excluded tomorrow. Ultimately, cybersecurity insurance works best when treated like a fire extinguisher: essential to have, better if never used, and useless without proper prevention measures already in place. In 2025’s dangerous digital landscape, the wisest strategy is to invest in both strong defenses and the right Cybersecurity Insurance, because when it comes to cyber threats, it’s not about if, but when.










Very detailed. Thanks for sharing
Excellent.. thank you so much..
This is a useful article.